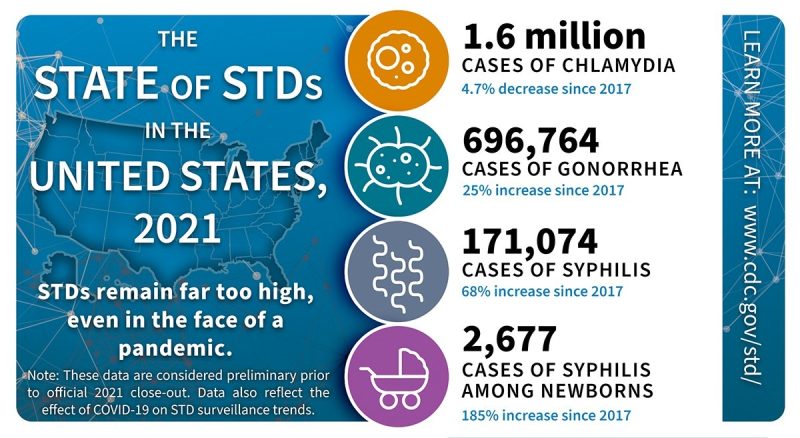
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reported in a news release in April of 2021 that there had been a rise in US cases of STDs in 2019, marking six consecutive years of increasing cases of sexually transmitted infections. While there was a temporary decline in reported cases during the start of the pandemic, health officials believe this was due to a decrease in the availability of STD testing services. They note the surge of reported STD cases as testing clinics were able to re-open after the disruption to some health care services brought on by the pandemic. The increase in recent years is likely due to several factors; the CDC news release cites drug use, poverty, and unstable housing as contributing factors. Even online dating sites have been proposed as a possible factor.
Some of the more serious consequences from STDs include an increased risk of getting HIV, chronic pelvic pain, infertility, and complications for newborns—including death. Due to these health complications and the increase in rates of STIs, the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services devised a Sexually Transmitted Infections National Strategic Plan (STI Plan): 2021—2025. In an effort to reverse the trend, the plan outlines strategies to prevent new STIs, improve treatment, advance STI research, reduce STI health disparities, and achieve coordinated efforts to address the STI epidemic.
UW Resources
General Resources
- Strange Bedfellows: Adventures in the Science, History, and Surprising Secrets of STDs – 2021 print book.
- 6 Things You Don’t Know (But Should) About STIs – UW Medicine Right as Rain article, Feb. 2020.
- Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs) – UW Medicine patient education page.
- UW Sexual Health information page, including where to get:
- Free safer sex supplies: mail order to home or pick up at Hall Health.
- Confidential STI testing and treatment.
- PrEP (pre-exposure prophylaxis) prescription medication for people at risk of HIV to help prevent HIV transmission.
- HPV vaccination.
Clinicians
- National STD Curriculum – University of Washington free educational website which includes lessons for CNE/CME credit as well as a library of STD podcast episodes.
- The University of Washington STD Prevention Training Center – From the website: Dedicated to increasing the knowledge and skills of healthcare providers in the area of sexual health.
- Teaching Young Men About Sexually Transmitted Infections –2014 instructional video from the series, Reaching Teens: Strength-Based Communication Strategies to Build Resilience and Support Healthy Adolescent Development.
- Sexually Transmitted Disease and Male Infertility: A Systematic Review – European Urology Focus journal article Oct. 2016
- Sexually Transmitted Infection Knowledge among Older Adults: Psychometrics and Test–Retest Reliability – International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health article, Apr. 2020.
- Time in Jail or Prison Is Associated with an Increased Risk of STDs – Perspectives on Sexual and Reproductive Health article, Sept. 2011.
Local & State Resources
- King County HIV and STD testing – Provides information on testing locations including at-home testing options.
- Sexually Transmitted Disease (STD) – Washington State Department of Health STD & STI data and fact sheets.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
For Providers
- Expedited Partner Therapy – STD treatment and screening page.
- Training – STD training page includes webinars, flashcards, clinical slides, prevention courses.
- Laboratory Information – Includes how to request laboratory testing through CDC.
For General Public (fact sheets also in Spanish)
Image credit: Division of STD Prevention, National Center for HIV, Viral Hepatitis, STD, and TB Prevention, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2022). The State of STDs – Infographic. Retrieved September 30th, 2022 from the CDC